Table of Contents
What is Islamophobia?
Islamophobia means having an unfair fear or dislike of Islam and its followers. It often shows up as bad opinions or actions toward Muslims and their way of life. The word “Islamophobia” was made in the late 1900s by joining the words “Islam” and “phobia,” which means fear. This shows that the fear is not based on facts. To stop Islamophobia, it’s important to understand where it comes from and what causes it to spread, especially in Western countries.
Islamophobia has a long history and comes from stories and events that make Muslims look bad. A big turning point was after the September 11 attacks in 2001, led by Osama Bin Laden. After that, many people started to fear and blame Muslims. They were often unfairly seen as terrorists or dangerous. These ideas spread through the news, politics, and everyday conversations. This made fear and hate toward Muslims grow even more in some parts of society.
Islamophobia can show up in different ways. Sometimes it’s very clear, like hate crimes or people saying hurtful things. Other times, it’s more hidden, like unfair treatment at work or being left out because of religion. In Western countries, these actions often come from not understanding Muslim culture or beliefs. This causes people to believe wrong things about Islam. Because of this, many Muslims feel left out or treated unfairly. To stop Islamophobia, people need to admit it’s real and work to create a world where everyone’s beliefs are respected and understood.
Historical Background of Islamophobia
Islamophobia has been around for a long time and comes from history shaped by politics, society, and culture. People started using the word more in the late 1900s, but negative views about Islam began much earlier. One major event that caused this was the Crusades, which happened between the 11th and 13th centuries. During that time, there were many battles between Christians and Muslims. Muslims were often shown as violent and extreme, and these wrong ideas created stereotypes that lasted for many years.
Looking back in history, we see that colonialism in the 1800s and early 1900s made Islamophobia even stronger in Western countries. The powerful countries that took control of others often described the cultures and religions they ruled, like Islam, as weak or not good enough. They did this to make their control seem right or fair. Books, art, and early newspapers also helped spread wrong ideas about Islam. These false pictures and stories added to the unfair treatment of Muslims that we still see today.
Today, Islamophobia has become more common, especially after the September 11 attacks in 2001. That event changed how many people think and talk about Islam. Since then, some have wrongly connected the religion mostly with violence and terrorism. This has caused many Muslims in Western countries to face unfair treatment and hate. They are often judged by old stereotypes. To fight Islamophobia, it’s important to understand where these wrong ideas came from and how they still affect people today.

Causes of Islamophobia
It is a complex problem that happens for many reasons, especially in society and politics. One big reason is the way some politicians talk, especially during elections. To get more support, they sometimes use people’s fear of terrorism and safety. They may say things that make Muslims seem like a threat. This makes people more afraid and less trusting. Because of this, some governments make rules that treat Muslim communities unfairly, making the problem even worse.
The media also plays a big role in how people see Islam. Many news channels focus on shocking stories that show extreme actions by a few people. They often leave out the normal lives and good things that Muslims do every day. Because of this, some people start to believe that all Muslims are violent or dangerous. These wrong ideas create fear and lead to Islamophobia, where people judge all Muslims based on what they see in the news.
Money problems in some areas also add to Islamophobia. When people are struggling to find jobs or get help, they sometimes blame others. Muslims can be unfairly seen as taking jobs or resources. This causes tention and makes people more likely to believe negative things about Islam. On top of that, social media often spreads false information. Many people don’t really understand what Islam teaches or know how different Muslim people can be. This lack of knowledge leads to fear, confusion, and unfair treatment.
A big reason Islamophobia continues is that many people don’t have good education about Islam. They don’t learn the truth and only hear wrong or negative things. That’s why it’s so important to teach understanding and kindness. By learning more about Islam and respecting different cultures, people can help stop fear and hate. This can help build a world where differences are accepted and everyone feels included.
Impact of Islamophobia on Society
Islamophobia causes serious problems for people and communities in the western world.It hurts people emotionally, socially, and even financially. Many face unfair treatment, which makes it harder for everyone to live together peacefully. One of the most worrying parts is the rise in hate, like bullying, rude comments, and even physical attacks. These things not only make people feel scared at the moment, but they can also damage a person’s self-confidence and make them feel like they don’t belong.
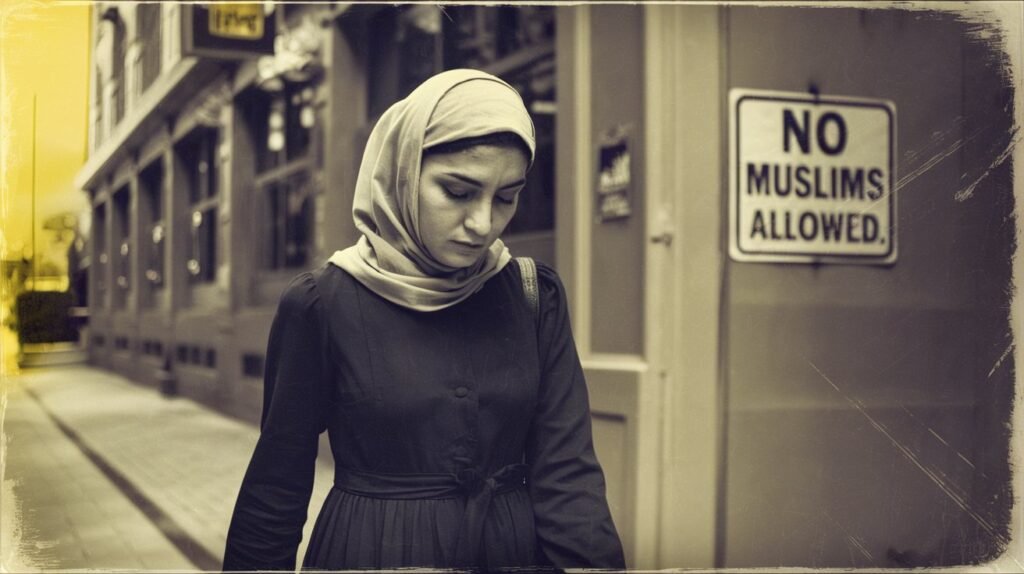

Hate crimes against Muslims have been rising, creating fear and anger in many communities. People who go through these attacks often feel very hurt and scared. This can lead to serious mental health problems like anxiety, depression, or PTSD. Many Muslims begin to fear showing their true identity, and some stop taking part in public life. This emotional pain doesn’t just affect one person it can hurt entire communities and create lasting divisions between people for many years.
It also causes problems with jobs and money for many Muslims. Some employers may treat Muslims unfairly, even without realizing it. They might not give them jobs or promotions just because of their religion. This keeps many Muslim families stuck in poverty and feeling left out. Muslim-owned businesses can also be hurt by boycotts or damage, which hurts not only those businesses but the whole local economy. These unfair actions spread the wrong idea that an entire religion is bad, which makes the problem even worse.
All these problems show why it’s so important to understand and fight against Islamophobia.To build a better society, people need to learn to respect different cultures and religions.When communities come together and support each other, it helps reduce fear and hate. In short, stopping Islamophobia is necessary to protect people’s well-being and to create peace and unity in our communities.
Islamophobia in the Media
The media has a big influence on how people think, especially about different groups like Muslims. Sadly, Muslims are often shown in a negative way in the news and other media.Many reports focus too much on scary or violent stories and don’t show the full truth.This can lead to unfair ideas and stereotypes about all Muslims. When only the bad side is shown, people may start to believe that the whole community is dangerous, which adds to the problem of Islamophobia in the western world.
News channels are often blamed for using words that unfairly connect Islam to terrorism, without explaining the full story. This kind of reporting makes people scared and builds wrong beliefs about Muslims. Strong and emotional headlines can make viewers judge all Muslims too quickly, turning a group with many different people into one negative image. These unfair ideas don’t just stay in the news-they also show up in movies and TV shows, where Muslims are often shown as villains or dangerous people. This adds to the spread of Islamophobia.
In many popular movies, Muslim characters are often shown as either extremists or helpless victims. This doesn’t show the real variety of people in the Muslim community. These one-sided images can make people believe wrong things, especially if they don’t personally know any Muslims. Since people watch a lot of media in the western world, it’s very important to fix these unfair pictures. We need more fair and true stories that show the different ways Muslims live. When people see better media, it can help stop Islamophobia and create more respect and understanding.
Islamophobia in Politics
Politics in the western world has changed in ways that sometimes make Islamophobia worse. What politicians say can strongly affect how people feel about Muslims. Some leaders and political groups use words that blame or target Muslims just to get more votes. During elections, we often hear messages that make Muslims seem like outsiders or dangers to society. This kind of talk can create fear and lead to unfair treatment of Muslim communities.
Laws made by governments, both big and small, often add to these negative feelings. For example, some security laws focus too much on Muslim communities, leading to more spying and police checks on them. These actions don’t see the many different types of Muslims and make them feel left out and not trusted. This kind of thinking doesn’t just stay in the law-it spreads through society and makes people more likely to accept Islamophobia as normal.
Political speeches often show how people’s opinions are changing. Some leaders use fear about terrorism or immigration to get support for their own goals. During elections, Muslims are sometimes shown in a bad way, making them seem dangerous or untrustworthy. This unfair picture spreads false stories and stereotypes. People who don’t know much about Islam may believe these things and form the wrong ideas about Muslims.
Countering Islamophobia
In the past few years, more people have seen the need to stop Islamophobia, especially in the western world where many still believe wrong things about Islam and Muslims. Different methods are now being used to fight this unfair treatment and create a more welcoming and understanding society. One important way is through community outreach. Local groups and religious organizations have started programs where people from different backgrounds can meet, talk, and learn from each other. These small, local efforts help break down false ideas by showing the true and peaceful side of Islamic culture.
Education is also very important in stopping Islamophobia. Many schools and colleges now teach about the history, beliefs, and good contributions of Muslim people. These lessons help students learn the truth, think carefully, and understand different cultures. There are also workshops and training programs that help people talk to others from different backgrounds. These programs teach people to notice their own biases and help them become more open, kind, and accepting of others in society.
Talking between people of different religions is another good way to fight Islamophobia. These talks help people learn from each other and understand different beliefs. Many times, they find they have similar values and experiences. This helps them stand together against hate and unfair treatment. It’s also important to have fair laws. Leaders should make rules that protect everyone from hate crimes and make sure all people are treated equally, no matter what religion they follow.

In the end, stopping Islamophobia needs many different efforts working together. We need to bring communities together, teach people the truth, have talks between different religions, and support fair laws. These steps are very important to help people understand each other and build a world where everyone is respected, no matter their religion.
The Role of Education in Reducing Islamophobia
Education is a very important way to fight Islamophobia and help people in the western world understand Islam better. Schools can teach not just what Islam believes, but also its long history and the many good things Muslims have done for society. This helps break the wrong ideas that cause fear and hate. When people learn the truth, they are less likely to believe false things or treat others unfairly.Teaching everyone the facts can help stop discrimination before it starts.
Schools are very important in teaching young people how to think about others. Teachers should give the right information about Islam, showing that it teaches peace, kindness, and helping others. Fun and interactive activities like workshops, talks, and group discussions can help students from different backgrounds talk and learn from each other. Meeting and talking with real Muslims helps students understand them better and respect their faith.This kind of learning can help remove fear and wrong ideas about Islam.
Besides learning in schools, community programs and public awareness campaigns can help people of all ages understand Islam better.Books, documentaries, and websites can teach both kids and adults who might have wrong ideas about Muslims. These tools help break stereotypes and show the true side of Islam and its followers. When people learn the truth, it can help reduce fear and bring more peace and respect in society.